When Is It Too Late For Gum Grafting? – Everything You Need To Know
Gum grafting is important to maintain healthy gums and protect your teeth from further damage. As with many medical treatments, timing can be a factor in effectiveness. The condition of your gums and overall dental health can influence your options and outcomes.
Knowledge about the timing of gum grafting involves considering different aspects of your oral health. With various factors at play, knowing when it’s appropriate to proceed with this treatment is very important. Let’s talk about these considerations to help you make the best decisions about your gum health and the best path forward.
Why I Need A Gum Graft?
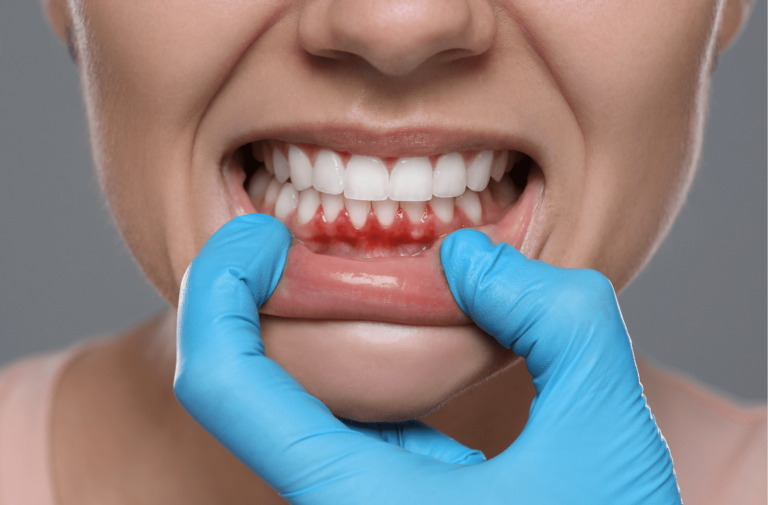
You need a gum graft when you experience gum recession. This condition can lead to sensitivity and an increased risk of decay. Factors like periodontal disease, aggressive brushing, or genetic predisposition can cause gum recession.
The procedure helps you to restore the gumline, protect the roots, and improve overall oral health. Also, gum grafting improves the appearance of your smile and prevent further gum loss.
When Is It Too Late For Gum Grafting?
It’s too late for gum grafting if the underlying bone structure has been significantly compromised. If gum recession has advanced to a point where there is severe bone loss or the teeth are loose, the procedure may no longer be effective. Also, if you have certain health conditions that affect healing, it may be too late to benefit from a graft.
Signs That Indicate It Might Be Too Late
Severe Gum Recession:
Extensive exposure of tooth roots with significant gum loss.
Loose Teeth:
Teeth that feel unstable or shift position.
Advanced Bone Loss:
Significant deterioration of the bone supporting your teeth, visible on X-rays.
Chronic Symptoms:
Persistent gum pain, sensitivity, or bleeding despite other treatments.
Risks Of Delaying Gum Grafting
Worsening Gum Recession:
Progressive gum loss exacerbates the problem.
Increased Bone Loss:
Further deterioration of the supporting bone structure.
Higher Sensitivity:
Greater discomfort and sensitivity of exposed tooth roots.
Increased Risk of Cavities:
Higher likelihood of tooth decay due to exposed roots.
Potential Tooth Loss:
Greater risk of losing teeth if the supporting structures are severely damaged.
Can Any Doctor Do A Gum Graft?
Not all doctors can perform gum grafting. This procedure is typically done by periodontist. While some general dentists may offer gum grafting, it is best to consult a periodontist for this specialized procedure to ensure the highest level of expertise and care.
Importance Of Choosing A Qualified Professional
Expertise:
A periodontist has specialized training and experience in gum procedures, leading to better outcomes.
Precision:
Specialists are more adept at performing precise surgical techniques, reducing the risk of complications.
Comprehensive Care:
Periodontists can provide a thorough evaluation and personalized treatment plan tailored to your specific needs.
Advanced Techniques:
They often have access to the latest technology and methods, ensuring the most effective treatment.
When Is It Too Late To Reverse Gum Disease?
It is too late to reverse gum disease once it has progressed to advanced periodontitis. At this stage, significant bone loss, deep periodontal pockets, and loose teeth are present, making reversal impossible. Treatment can manage symptoms and prevent further damage but cannot fully restore lost structures.
Stages Of Gum Disease
1. Gingivitis:
The earliest stage is characterized by red, swollen gums that bleed easily.
2. Early Periodontitis:
Mild bone loss and gum recession, with pockets forming around the teeth.
3. Moderate Periodontitis:
Increased bone loss, deeper pockets, and potential tooth mobility.
4. Advanced Periodontitis:
Severe bone loss, deep pockets, loose teeth, and possible tooth loss.
Early Signs And Symptoms
Red Swollen Gums:
Inflammation and discoloration of the gum tissue.
Bleeding Gums:
Bleeding during brushing or flossing.
Bad Breath:
Persistent bad breath or a bad taste in the mouth.
Gum Recession:
Gums pull away from the teeth, making them appear longer.
Treatment Options For Gum Disease
Non-Surgical Treatment
Scaling and Root Planing:
A deep-cleaning method involves scraping away plaque and tartar from below the gum line and smoothing the tooth root to remove bacterial toxins.
Antibiotics:
Both topical and oral antibiotics can be used to control bacterial infection. These include mouth rinses, antibiotic gels, and pills.
Laser Therapy:
Lasers are used to remove inflamed gum tissue and bacteria, which helps reduce pocket depth and promote healing. After initial treatment, more frequent professional cleanings are necessary to maintain gum health and prevent disease progression.
Surgical Treatment
Flap Surgery :
The gums are lifted back to remove tartar and then sutured back so they fit tightly around the teeth, reducing the size of the pockets.
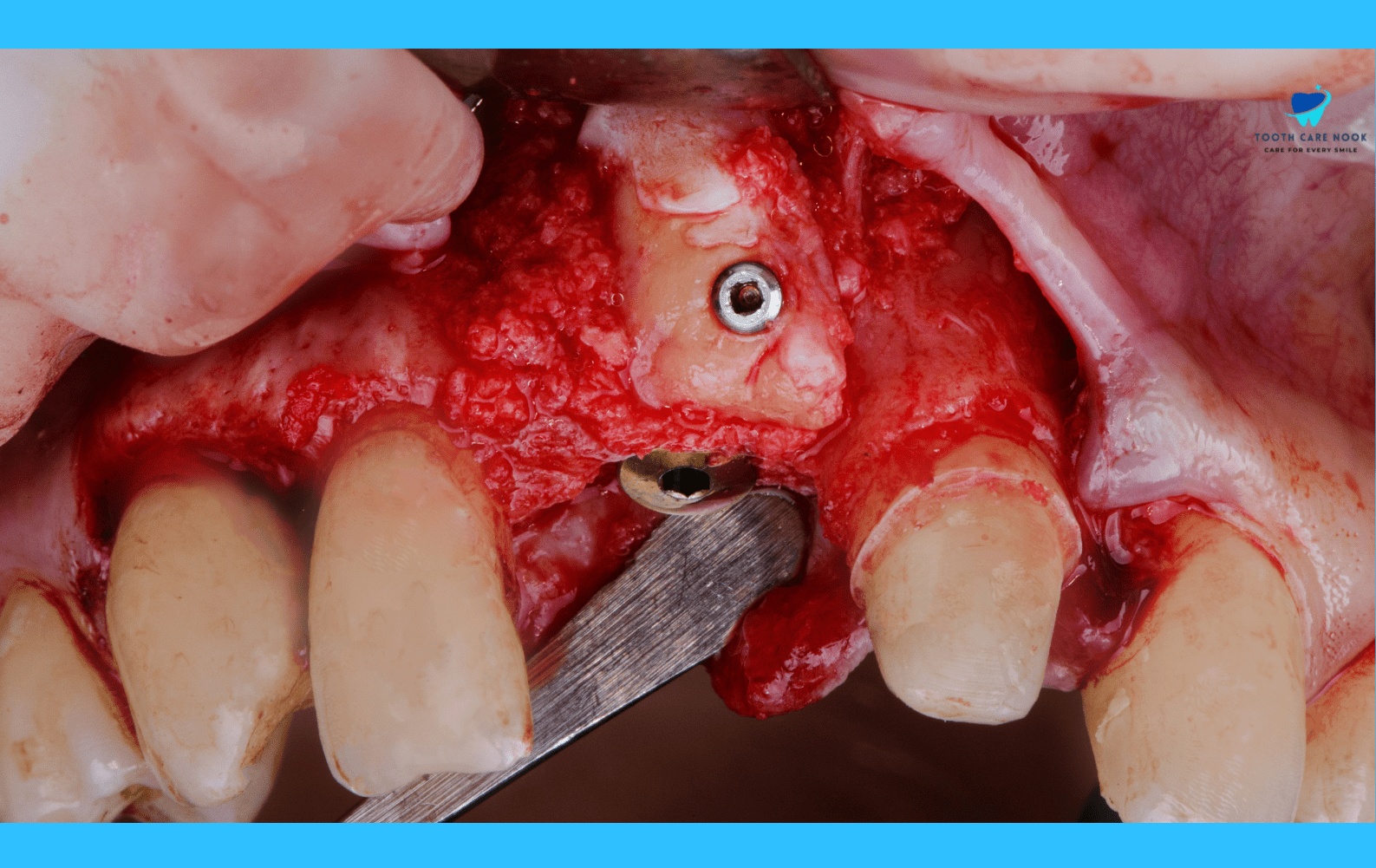
Bone Grafts:
This procedure involves using bone from your own body, a synthetic source, or a donated source to replace bone destroyed by gum disease and promote new bone growth.
Soft Tissue Grafts:
Tissue from the roof of your mouth or another donor source is used to cover exposed roots, reduce gum recession, and improve the appearance of the gumline.
Guided Tissue Regeneration:
A small piece of mesh-like material is inserted between the bone and gum tissue to prevent the gum from growing into the area where the bone should be, allowing the bone and connective tissue to regrow.
Tissue-Stimulating Proteins:
Applying a special gel to a diseased tooth root can stimulate the growth of healthy bone and tissue, aiding in the regeneration of the gums.

FAQs
Do Gum Grafts Work?
Yes, gum grafts are effective. They can restore the gum line, cover exposed roots, and protect against further recession and decay. The success rate is high when performed by a qualified periodontist.
Is Gum Grafting Necessary?
Gum grafting is necessary if you have significant gum recession or exposed roots, or if your dentist determines that it’s needed to prevent further oral health issues. It can also be necessary to improve the aesthetics of your smile.
Does Gum Graft Help Loose Teeth?
Gum grafting can help stabilize loose teeth by strengthening the gums and supporting the underlying bone. However, the overall stability of loose teeth depends on the extent of bone loss and other factors.
When Do You Need A Gum Graft?
You need a gum graft when you have severe gum recession, exposed tooth roots, or when other treatments have not effectively managed the condition. A periodontist will assess your situation to determine if gum grafting is the appropriate treatment.