What is Hypocalcification Teeth | Types, Causes and Treatment
We all dream of a picture-perfect smile, but sometimes reality throws us a curveball. You expect different dental problems like hypocalcification teeth. You look for information and solutions to manage this condition effectively as dental awareness grows.
Don’t worry, you’re not alone! Many people experience these unexpected dental issues, leaving them wondering what’s causing the issue. In this article, we’ll get to know about the hypocalcification of teeth, its types, causes, and treatment options. Let’s start with what exactly hypocalcification teeth are.
What Is Hypocalcification Teeth?
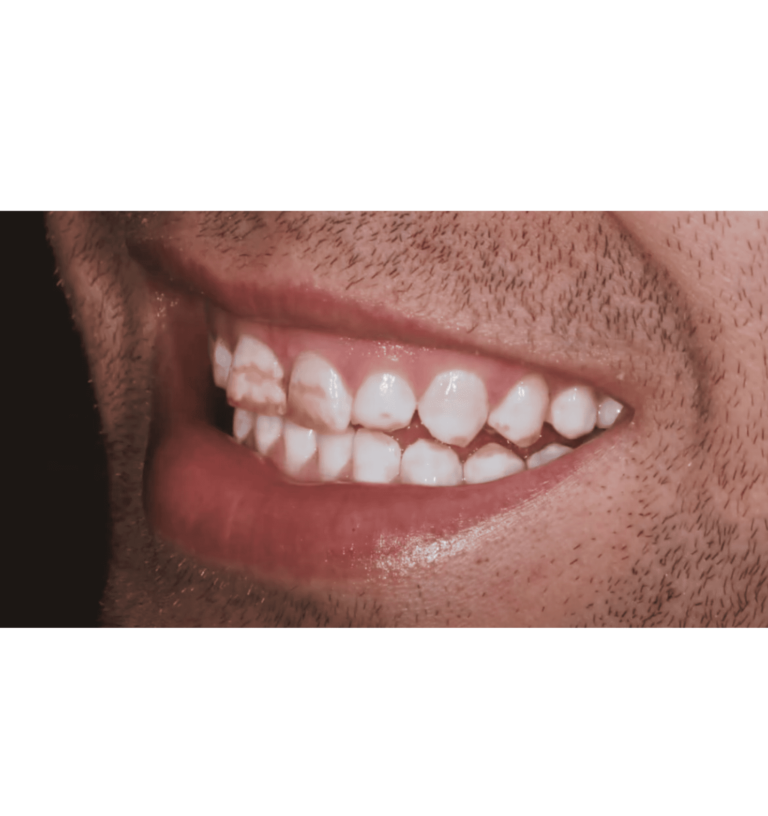
Hypocalcification teeth are teeth with insufficient calcium content which leads to weak and porous enamel. This condition results in white or brown spots on the tooth surface and makes the teeth more vulnerable to decay and damage.
It’s first noticed in children as their teeth develop, but adults can also be affected. Hypocalcification can significantly impact your dental health and appearance.
Types Of Teeth Hypocalcification
Enamel Hypoplasia
Enamel hypoplasia is the incomplete or insufficient development of enamel. Affected teeth can be smaller than usual and more prone to damage. This type of tooth hypocalcification can result from nutritional deficiencies, illness, or trauma during tooth development. Teeth with hypoplasia often have grooves, pits, or missing sections of enamel.
Enamel Aplasia
Enamel aplasia is characterized by a complete lack of enamel in certain areas of the teeth. The underlying dentin is exposed which increases tooth sensitivity and susceptibility to cavities. This condition can make the teeth appear yellow or brown due to the exposed dentin. It can significantly affect dental health and aesthetics.
Focal Enamel Opacities (FOE)
Focal enamel opacities occur in localized areas of the enamel. These spots can be white or have a darker hue which varies in size and shape. They are often less extensive than diffuse opacities but can still impact the appearance and strength of the teeth. FOE can result from localized trauma or disturbances during enamel formation.
Incisor-Molar Hypomineralization (MIH)
MIH affects the first permanent molars and permanent incisors. It is characterized by enamel with a dull appearance and coloration ranging from yellowish-white to brown. The exact cause of MIH is not fully understood, but it is thought to be related to early childhood health issues.
Diffuse Enamel Opacities (DDE)
Diffuse enamel opacities are generalized areas of opacity in tooth enamel. These areas can vary in size, shape, and coloration which ranges from milky white to yellow or brown. DDE is often associated with systemic conditions or environmental factors during enamel formation. The extent and severity of opacities can vary widely among individuals.
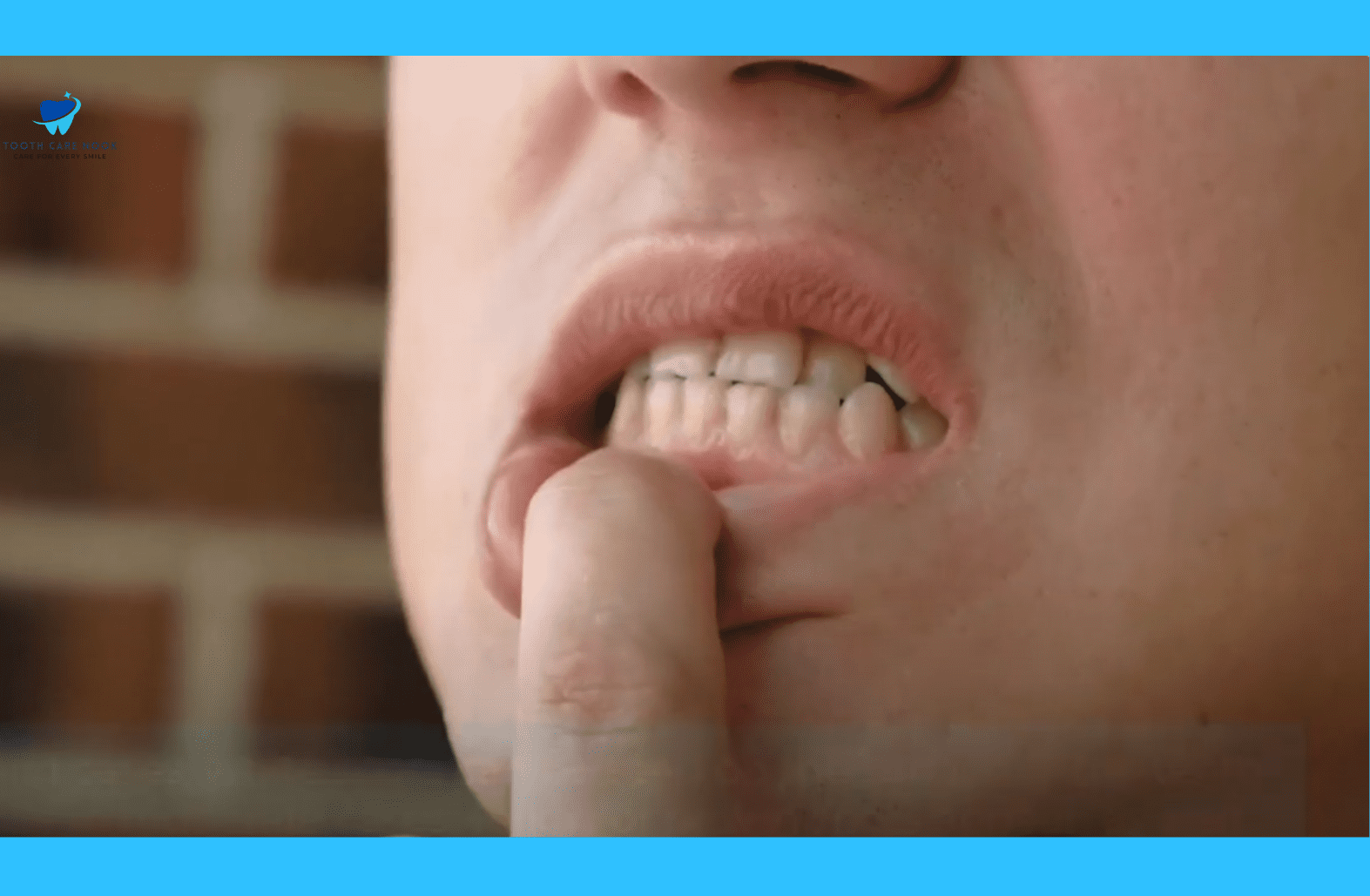

Causes Of Hypocalcification of Teeth
The following are some main causes of hypocalcification of teeth:
Nutritional Deficiencies
A lack of essential nutrients like calcium, vitamin D, and phosphorus during tooth development can cause hypocalcification. These nutrients are a must for proper enamel formation and mineralization. Poor nutrition during childhood, when teeth are developing can result in weaker enamel.
Childhood Illnesses and Fevers
High fevers and illnesses during early childhood can disrupt enamel formation. Conditions like chickenpox, measles, or frequent infections can affect the developing teeth. The stress on the body during illness can interfere with the proper mineralization of enamel. This can lead to areas of hypocalcified enamel that are more susceptible to decay.
Excessive Fluoride Exposure
Consuming too much fluoride during tooth development can cause dental fluorosis. This condition results in white spots or streaks on the teeth, and in severe cases, brown discoloration. Excessive fluoride intake can occur from drinking water with high fluoride levels or overuse of fluoride toothpaste. Monitoring fluoride intake is important for preventing fluorosis.
Environmental Factors
Exposure to certain environmental factors like lead or other heavy metals can affect enamel formation. Pollutants and toxins can interfere with the body’s ability to properly mineralize teeth. This can result in hypocalcification teeth that are more prone to decay. Reducing exposure to environmental toxins is crucial for dental health.
Poor Oral Care
Ignoring proper oral hygiene e.g. inadequate brushing and flossing can lead to plaque buildup. Plaque contains bacteria that produce acids that can erode enamel over time. Without regular brushing and dental care, these acids can weaken the enamel which increases the risk of hypocalcification of teeth.
Acid from Plaque
Acids from plaque combined with acids from acidic foods and beverages in your diet can further damage tooth enamel. Sugary and acidic foods can create an acidic environment in the mouth which promotes enamel erosion. Over time this acidic assault can contribute to hypocalcification and tooth decay.
Hypocalcified Teeth Treatment
Here are some hypocalcified teeth treatment options:
Fluoride Treatment
Fluoride application helps strengthen hypocalcified structures of enamel and prevent further decay. Professional fluoride treatments or fluoride-containing toothpaste can be recommended by a dentist. Fluoride works by remineralizing the enamel which makes it more resistant to acid attacks.
Dental Sealants
Sealants create a barrier that seals out bacteria and food particles which reduces the risk of enamel erosion. Sealants are often recommended for molars which are more prone to decay.
Composite Bonding
Composite bonding helps restore the appearance and strength of hypocalcified enamel. Bonding can also fill in pits or grooves in the areas of hypocalcification teeth enamel which improves the tooth’s resistance to decay.
Crowns or Veneers
In severe cases of dental hypocalcification, crowns or veneers are necessary to protect and strengthen the teeth. Crowns cover the entire tooth surface while veneers are thin shells placed over the front of the teeth. Both options can provide durable protection and improve aesthetics.
FAQs
Is Hypocalcification The Same As Decalcification?
No, hypocalcification and decalcification are not same. Both involve changes in enamel mineralization, hypocalcification is primarily a developmental issue while decalcification is related to poor oral hygiene and bacterial activity.
What Is The Difference Between Incipient Caries And Hypocalcification?
Incipient caries are early decay spots caused by bacterial acid on the other hand, hypocalcification is a developmental issue that leads to poorly mineralized enamel.
Is Hypocalcification Intrinsic?
Yes, hypocalcification is considered intrinsic. Because it originates from internal developmental issues affecting enamel formation.
What Is Hypocalcification After Teeth Whitening?
Hypocalcification after teeth whitening refers to the appearance of white spots or patches on the enamel that become more noticeable after the whitening process. Teeth whitening does not cause hypocalcification of teeth but can highlight these intrinsic enamel defects.