How Long Does Temporary Dental Cement Last?
Temporary dental cement lasts for a few weeks. It depends on factors such as the type of cement used, the extent of dental work, and individual oral hygiene habits.
While temporary cement is designed to provide a temporary fix for dental restorations such as crowns, bridges, or veneers, it is not intended for long-term use. Over time, temporary dental cement may degrade or wear down due to factors like chewing forces, saliva, and exposure to oral fluids.
How to Use Dental Cement?
Here are the steps for the usage of dental cement:
Apply the Cement:
Make sure the dental cement is well-mixed according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Achieve a smooth, homogenous consistency for proper application.
Use an applicator or spatula to place a small amount of cement onto the inner surface of the restoration. Avoid excessive application to prevent overflow.
Position the Restoration:
Carefully place the restoration onto the prepared tooth surface to ensure proper alignment and fit. Apply gentle pressure to seat the restoration fully.
Remove Excess Cement:
With the help of a dental floss or an interdental brush remove any excess cement that may have extruded from the margins of the restoration. Thorough removal helps prevent irritation and ensures a clean finish.
Hold in Place:
Maintain gentle pressure on the restoration for the recommended setting time. This allows the cement to bond securely to both the restoration and the tooth surface.
After the cement has been set, evaluate the restoration for fit and occlusion. Make any necessary adjustments to ensure your comfort.
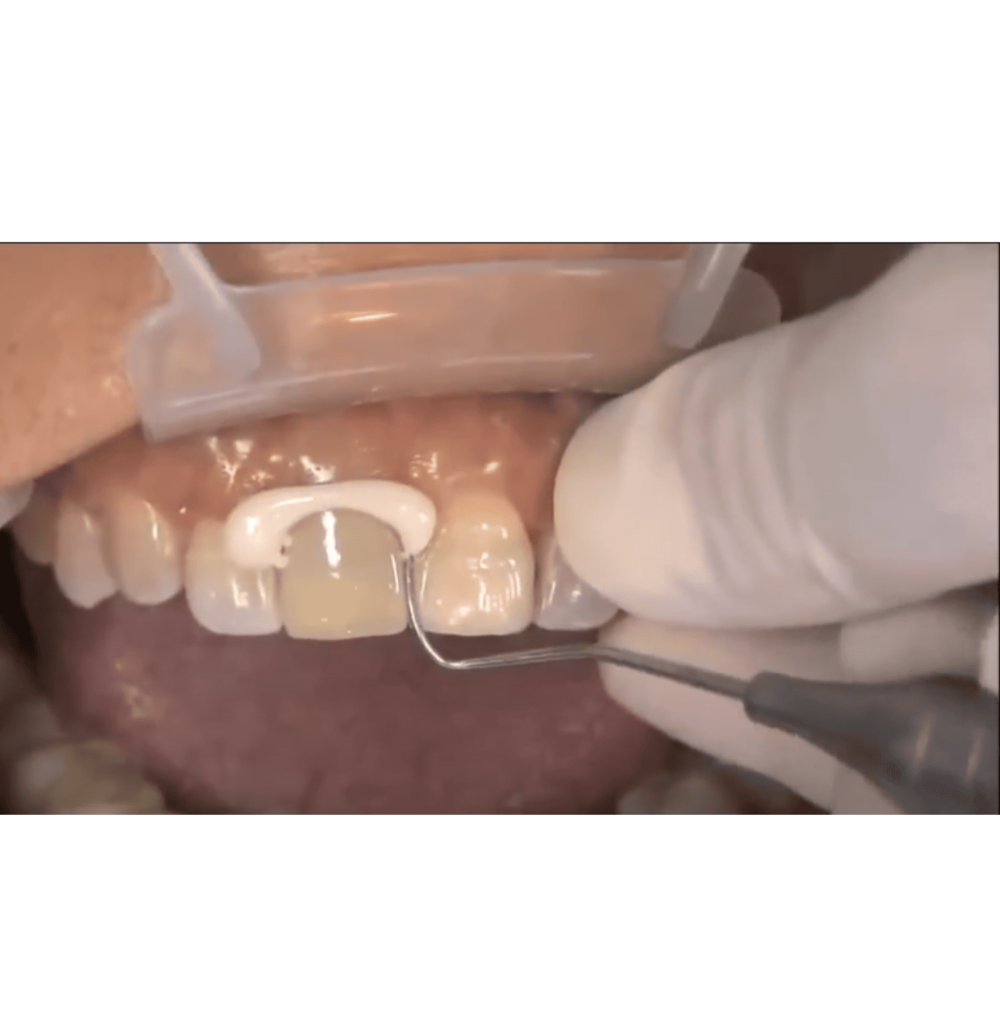
Is Temporary Dental Cement Strong?
Temporary dental cement is not as strong or long-lasting as permanent dental cement, but it offers sufficient strength and durability for short-term use.
It is formulated to withstand normal chewing forces and provide stability for the restoration until a permanent solution can be applied. However, it is not intended for long-term use.
Can You Eat With Temporary Dental Cement?
Yes, you can eat with temporary dental cement in place. While it offers sufficient strength for normal chewing forces. When eating with temporary dental cement, consider the following:
- Opt for softer foods that require minimal chewing, such as mashed potatoes, yogurt, or soup. Avoid hard, sticky, or crunchy foods that could potentially dislodge or damage the restoration.
- Do not bite down forcefully on the restoration, as this can increase the risk of dislodging or loosening the cement.
- After eating, gently rinse your mouth with water to remove any food particles or debris.
Does Temporary Dental Cement Dissolve?
Temporary dental cement does not dissolve in the same way as substances like sugar in water but instead undergoes a process of degradation over time due to exposure to oral conditions.
It contains ingredients such as zinc oxide, clove oil, or other resin-based materials. These components provide temporary adhesion and sealing properties but are susceptible to degradation due to exposure to saliva, food particles, and oral bacteria.
What Are The Disadvantages Of Temporary Cemented Dental Bridges?
Temporary cemented dental bridges come with the following disadvantages:
Temporary Discomfort During Eating:
Temporary bridges cannot provide the same stability and chewing efficiency as permanent ones. This can result in some temporary discomfort or difficulty while eating.
Limited Strength and Stability:
Temporary cemented bridges are generally less stable and durable than permanent bridges. They may not withstand heavy biting forces or prolonged wear which increases the risk of fracture or damage.
Risk of Decay and Gum Disease:
Temporary bridges may not fit as precisely as permanent ones which leave gaps where bacteria can accumulate. If oral hygiene is not maintained diligently, this can lead to tooth decay, gum disease, and potential damage to neighboring teeth.
Risk of Debonding:
Temporary cementing in teeth has weaker adhesive properties. As a result, temporary bridges are more susceptible to debonding or becoming dislodged, especially when subjected to chewing forces or trauma.
Maintenance Requirements:
Patients with a temporary cemented dental bridge need to be careful with their oral hygiene practices. They should avoid hard foods that could dislodge the bridge and follow specific cleaning instructions provided by their dentist to maintain oral health during the interim period.
How Long Does Permanent Dental Cement Last?
Permanent dental cement typically lasts for 10 to 15 years. With proper care and maintenance, it can offer lasting stability and retention for dental restorations.
How to Remove The Gold Crown From Extracted Tooth
Here are the steps involved in removing a gold crown from an extracted tooth :
-
Mechanical Methods:
Using dental instruments such as crown removers, crown splitters, or crown cutters to carefully break the bond between the crown and the underlying tooth structure. In this process, you require precision to avoid damaging the crown or causing trauma to the tooth.
-
Sectioning:
If the crown cannot be removed intact, it may be necessary to section it into smaller pieces using a dental bur or saw. This allows for easier removal of individual sections without compromising the surrounding tooth structure.
-
Chemical Dissolution:
In some cases, a chemical agent such as glue for dental bridge solvent can be used to soften the cement or bonding material which makes it easier to dislodge the crown. However, this method is less commonly used for gold crowns due to their resistance to chemical degradation.
-
Gentle Extraction:
Once the crown has been sufficiently loosened or sectioned, it can be gently lifted or pried away from the underlying tooth structure using dental instruments. Must be careful to avoid applying excessive force, which could cause damage to the crown or surrounding tissues.