What Are the Signs that Your Teeth Are Shifting? | A Guide
You may notice subtle changes in your teeth over time. These shifts can occur for different reasons. Teeth shifting can alter your bite, affect your smile, and even lead to discomfort or oral health issues if left unaddressed. Knowing why teeth shift and recognizing the early signs will help you take proactive steps to maintain your dental health.
Here we will talk about the specific signs of teeth shifting and how to address them effectively.
Signs Your Teeth Are Shifting
The following are some signs your teeth are shifting:
Crooked Teeth:
Noticeable changes in the alignment, where teeth that were once straight start to appear crooked.
Gaps Between Teeth:
New spaces appear between teeth that were not previously there.
Changes in Bite:
Discomfort or difficulty when biting or chewing due to altered teeth positioning.
Crowding:
Teeth appear closer together than before, often overlapping.
Speech Changes:
New difficulties in pronouncing words or developing a lisp.
Gum Sensitivity:
Increased sensitivity or discomfort in the gums, indicating underlying movement of the teeth.
Shifting Teeth Symptoms
Headaches:
Persistent or recurring headaches are often linked to jaw or bite misalignment.
Jaw Pain:
Pain in the jaw especially when opening or closing the mouth can be a sign of TMJ issues.
Neck and Facial Pain:
Pain extending from the jaw to the neck and facial muscles is a shifting teeth symptom.
Sensitive Teeth:
Increased sensitivity in teeth particularly when eating or drinking hot or cold substances.
Midline Shift:
Misalignment of the centerline of the teeth with the nose and chin, indicating teeth are shifting out of place.
New Gaps:
The development of spaces between teeth that were previously aligned is also a shifting teeth symptom.
Causes Of Teeth Moving
Here are the main causes of teeth moving:
Natural Aging Process:
As you age, your jaw muscles, ligaments, and the tissues around your teeth weaken, which can cause your teeth to loosen and shift. Also, changes in your facial features as you age can exert pressure on your teeth, pushing them inward.
Shifting Jawbones:
Your jawbones naturally shift throughout your life, and as you age, this movement can increase. An improper bite that develops from these alterations can push your teeth out of place. Aging can decrease the mineral content in your bones, weakening the support your teeth need to stay in place.
Missing Teeth:
Missing teeth can lead to teeth moving to fill the space which can affect the alignment of your bite.
Gum Disease:
Periodontal diseases can destroy the gum tissue and the jawbone, leading to tooth movement. This is one of the significant causes of teeth shifting.
Tongue Thrust:
An abnormal tongue positioning habit, where the tongue pushes against the teeth, can also cause teeth to shift, resulting in an open bite.
CPAP Therapy:
The pressure from CPAP machines used for treating sleep apnea can also lead to teeth shifting due to the pressure exerted on the teeth and jaw.
Dental Procedures:
Standard dental treatments like installing implants or bridges, removing teeth, or uneven fillings can create minor changes that might lead to tooth movement over time. Orthodontic treatments intentionally move teeth into better positions, but without proper aftercare like wearing retainers, teeth can shift back to their old positions.
How Long Does It Take For Teeth To Move?
The time it takes for teeth to move depends on the method of treatment and individual circumstances. For traditional braces, the average treatment duration ranges from one to two years.
For those using Invisalign or other clear aligners, teeth can move approximately 0.25 mm with each tray change, every two weeks. This means visible changes can occur within a month. The overall treatment duration with aligners can range from six months to a few years, depending on the severity of the dental corrections needed.
Why Do Teeth Shift With Age?
Natural Mesial Drift:
Over time, teeth naturally move towards the front of the mouth. Mesial drift is a gradual and natural occurrence that can lead to misalignments.
Changes in Bone Density:
As we age, our bones, including the jawbone, lose density. This weakening can cause teeth to shift as the support structure changes.
Periodontal Ligament Flexibility:
Teeth are held in place by the periodontal ligament, which is flexible and allows for some movement. Over time, factors like bruxism can enlarge the ligament and lead to more noticeable shifting.
Tooth Loss:
Missing teeth create gaps that can cause adjacent teeth to shift towards the space, altering alignment.
Habits That Can Cause Teeth To Shift
Bruxism:
Grinding or clenching your teeth, especially at night, can exert excessive pressure on your teeth. This can create small gaps and weaken the teeth, making them more susceptible to shifting due to daily activities like eating and drinking.
Poor Oral Hygiene:
Neglecting proper oral hygiene can lead to the buildup of plaque and tartar. This accumulation can cause gum disease, which weakens the support structures of your teeth, leading to potential shifting. Regular brushing, flossing, and dental check-ups are essential to prevent this.
Not Wearing a Retainer:
After orthodontic treatment, wearing a retainer is important to maintain teeth alignment. Failing to wear a retainer as instructed can cause teeth to shift back to their original positions over time.
Excessive Sugar Consumption:
A diet high in sugar can lead to tooth decay and gum disease, both of which can weaken teeth and their supporting structures, making them more prone to shifting.
Using Teeth as Tools:
Using your teeth to open packages, bite nails, or chew on hard objects can put undue stress on them, leading to movement and misalignment.
Overbite or Underbite:
Malocclusions like overbites or underbites can cause improper pressure distribution on teeth, leading to gradual shifting. Orthodontic treatments are often required to correct these issues.

How Long Does Teeth Shifting Pain Last?
Teeth-shifting pain lasts for a few days to a couple of weeks, depending on the individual and the extent of the movement. Mild discomfort may be experienced initially as the teeth adjust to their new positions. However, if the pain persists beyond a couple of weeks or becomes severe, it is advisable to consult a dentist or orthodontist for further evaluation and management.
How To Relieve Pain From Shifting Teeth
To alleviate pain from shifting teeth, you can try the following methods:
Over-the-counter Pain Relievers:
Non-prescription medications can help manage pain and reduce inflammation.
Cold Compresses:
Applying an ice pack to the outside of your cheek can help numb the pain and reduce swelling.
Orthodontic Wax:
If braces or other dental appliances are irritating, using orthodontic wax can provide relief.
Soft foods:
Eating softer foods can minimize discomfort while chewing.
Saltwater rinse:
Rinsing your mouth with warm saltwater can help soothe irritated gums and reduce pain.
What Does Teeth Shifting Feel Like?
Teeth shifting can be felt in several ways. Common sensations include a feeling of pressure or squeezing in the teeth, a general sense that the teeth are moving or rocking, and teeth feeling loosely anchored.
You might also experience tenderness, soreness, or an ache around the affected teeth, as well as sensitivity to hot, cold, and sweet foods. In some cases, pain or tension in the jaw muscles and discomfort while chewing can also be indicators of shifting teeth.
Is It Normal For Your Teeth To Move A Little?
Yes, it is normal for teeth to move a little over time. Teeth are not permanently fixed in place and can shift slightly due to various factors, including normal wear and tear, changes in the jawbone, and even daily activities like chewing. However, if you notice significant movement, increasing gaps, or discomfort, it could indicate an underlying issue that needs attention from a dental professional.
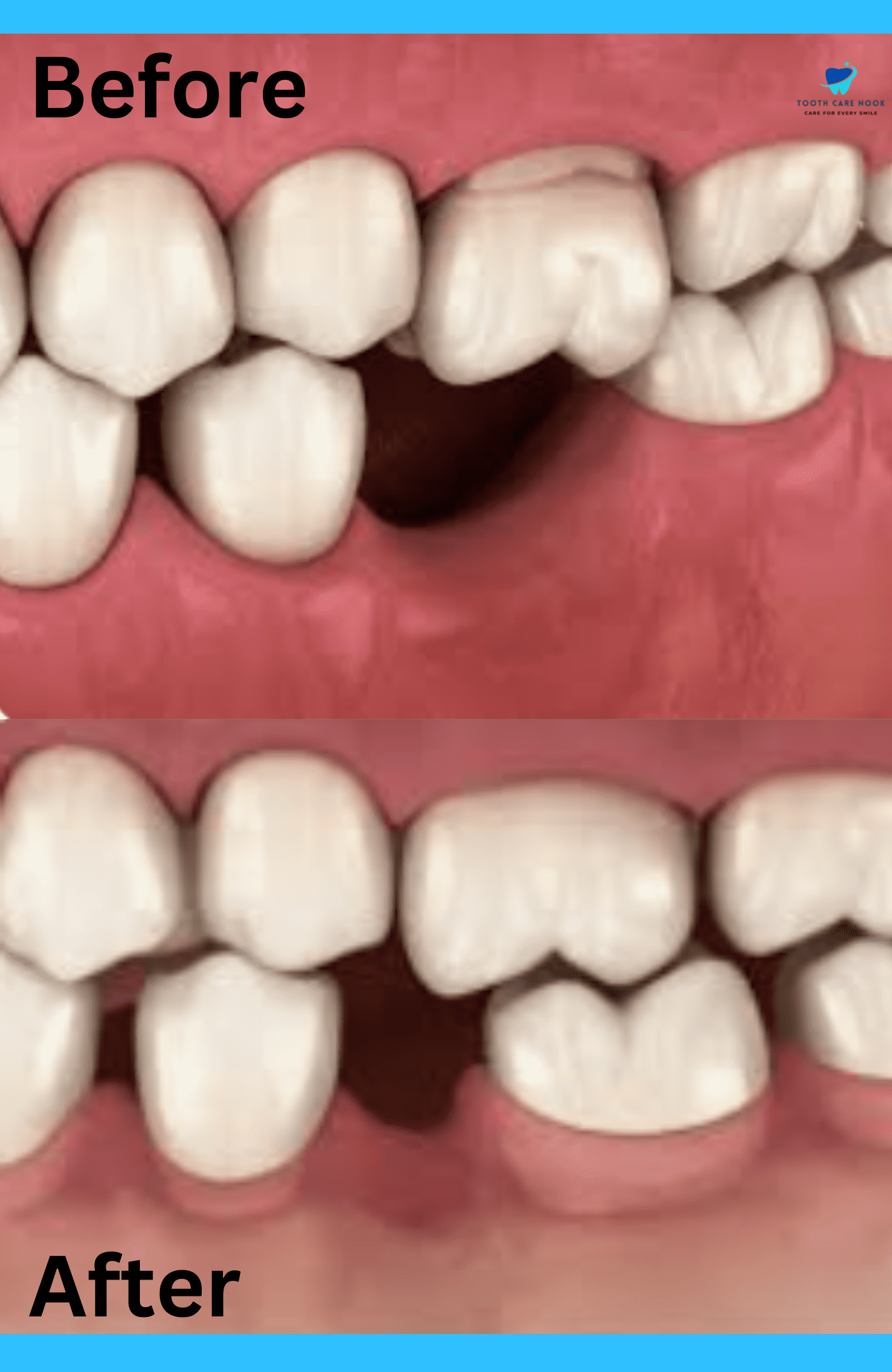
Teeth Shifting Before And After
Here are images showcasing teeth shifting before and after to help you understand the changes:
Relationship Between Gum Disease And Teeth Shifting
Gum disease can significantly impact teeth alignment. It begins with inflammation of the gums and can progress to periodontitis, affecting the bone supporting the teeth. This bone deterioration weakens the structural support that leads to teeth becoming loose and shifting. As gum disease advances, teeth may rotate or move out of place, creating misalignment issues.
How To Prevent Teeth From Shifting
Wear Retainers:
After orthodontic treatment, retainers are essential to keep your teeth in their new positions. They prevent your teeth from reverting to their original positions.
Address Tooth Loss Promptly:
If you lose a tooth, replace it immediately to prevent adjacent teeth from shifting into the gap. Dental implants or bridges are common solutions.
Correct Bite Issues:
Misaligned bites can cause teeth to shift over time. Orthodontic treatments, such as braces or aligners can help correct these issues.
FAQs?
Do Shifting Teeth Cause Pain?
Yes, shifting teeth can cause pain. This discomfort is often due to the pressure exerted on the teeth as they move. Symptoms can include soreness, sensitivity, and aching in the gums and jaw.
How Quickly Do Teeth Shift?
Teeth can begin to shift within days to weeks after changes such as tooth loss or stopping the use of retainers. For orthodontic treatments, noticeable teeth movement can occur within a few weeks, with the full treatment process taking several months to years, depending on the method and individual circumstances.
Can Shifting Teeth Cause Bleeding Gums?
Yes, shifting teeth can cause bleeding gums, especially if the movement is due to underlying gum disease. Inflammation and irritation from moving teeth can make gums more sensitive and prone to bleeding.
Can Teeth Shift Overnight?
Teeth do not shift overnight in a noticeable way. However, small, gradual movements can accumulate over time, leading to noticeable changes. Factors such as not wearing a retainer or engaging in habits like teeth grinding can contribute to these gradual shifts.
Why Do My Teeth Move?
Teeth can move due to a variety of reasons, including natural aging, gum disease, tooth loss, and orthodontic treatments. Habits such as teeth grinding and not wearing a retainer after braces can also cause teeth to shift. It’s important to address these factors early to maintain proper dental alignment.