What Is Intrusion Of Teeth? – Symptoms, Causes, Treatments And All
It can be puzzling and concerning to feel any unusual change in the position of your teeth. One such dental anomaly is the intrusion of teeth. This dental issue can affect both your appearance and the functionality of your bite. If you’ve noticed your teeth seem to move out of place or if you’re dealing with discomfort or difficulty while chewing, you should understand the reasons and potential treatments available.
What Is Intrusion Of Teeth?
Intrusion of teeth describes a situation where teeth get pushed inwards due to impact or trauma. This force pushes the teeth deeper into the jawbone socket which potentially damages the surrounding tissues and nerves.
Types Of Dental Intrusions
Simple Intrusion:
This is the most common type of dental intrusion. The tooth is pushed straight upper jaw or lower jaw into the bone socket but remains relatively upright.
Complex Intrusion:
In this case, the tooth gets displaced not only inwards but also sideways within the jawbone. This can cause more significant damage to the surrounding structures.
Extrusive Intrusion:
This is a less common type where the tooth gets pushed inwards initially but then rebounds slightly outwards to loosen it from the socket.
Causes Of Intruded Teeth
Falls:
Especially common in children, tripping or falling can cause a forceful impact on the face intruding on a tooth.
Sports Injuries:
Contact sports like football, hockey, or basketball increase the risk of facial trauma and intruded teeth.
Accidents:
Car accidents or other blunt force trauma to the face can cause intrusion of teeth.
Fights or Assaults:
Physical altercations can result in facial injuries, including intruded teeth.
Dental Procedures:
In very rare cases, dental procedures like tooth extractions or root canal treatments might accidentally intrude on a neighboring tooth.
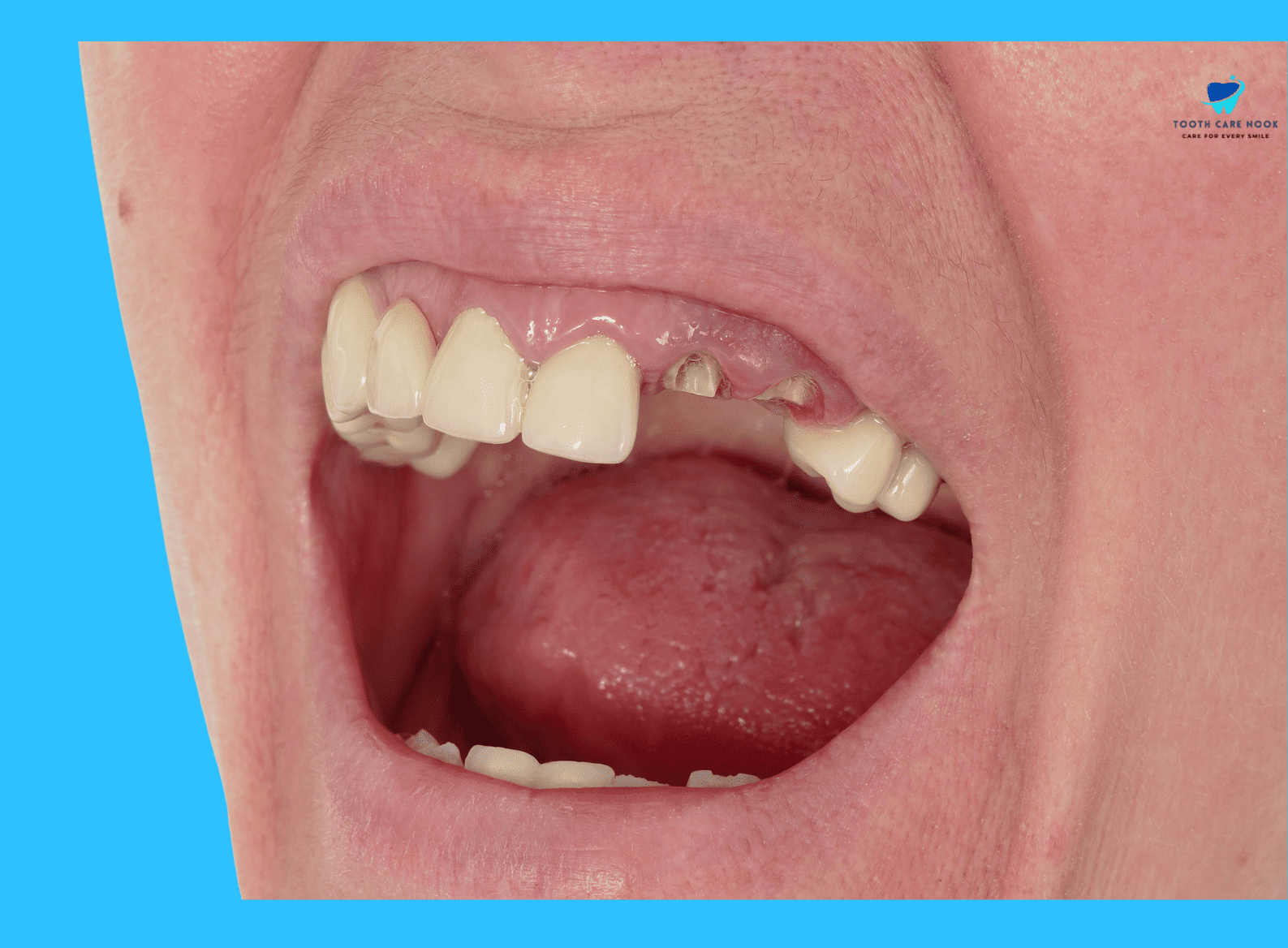
Signs And Symptoms
Loose tooth:
The intruded tooth may feel loose or wobbly when you touch it.
Pain:
You might experience pain or discomfort in the affected area, especially when biting or chewing.
Sensitivity:
The intruded tooth may become sensitive to hot or cold foods and drinks.
Shortened tooth:
The crown of the intruded tooth might appear shorter or partially hidden within the gum tissue.
Bleeding:
In some cases, there might be bleeding around the gumline of the intruded tooth.
Visible displacement:
The intruded tooth might be noticeably out of alignment with the surrounding teeth depending on the severity.
Treatment for Tooth Intrusion
Repositioning:
The dentist might attempt to reposition the tooth back to its original position if the dental intrusion is more significant. This can be done through orthodontic repositioning and surgical repositioning.
Splinting:
After repositioning, regardless of the method used, the tooth will likely be splinted to neighboring teeth for stabilization. Splints are made of flexible materials and help hold the tooth in place while it re-attaches to the bone socket. The duration of splinting will depend on the severity of the intrusion of teeth.
Root Canal Treatment:
Intrusion in permanent teeth with closed apices can damage the pulp (nerve and blood supply) inside the tooth. To prevent infection and preserve the tooth, a root canal treatment might be necessary. This involves removing the damaged pulp and sealing the canals within the root.
Extraction:
Unfortunately, in severe cases where the tooth is extensively damaged, fractured, or has a poor prognosis for survival, extraction might be the only option. Following extraction, a dentist will discuss potential solutions for replacing the missing tooth, such as implants, bridges, or dentures.
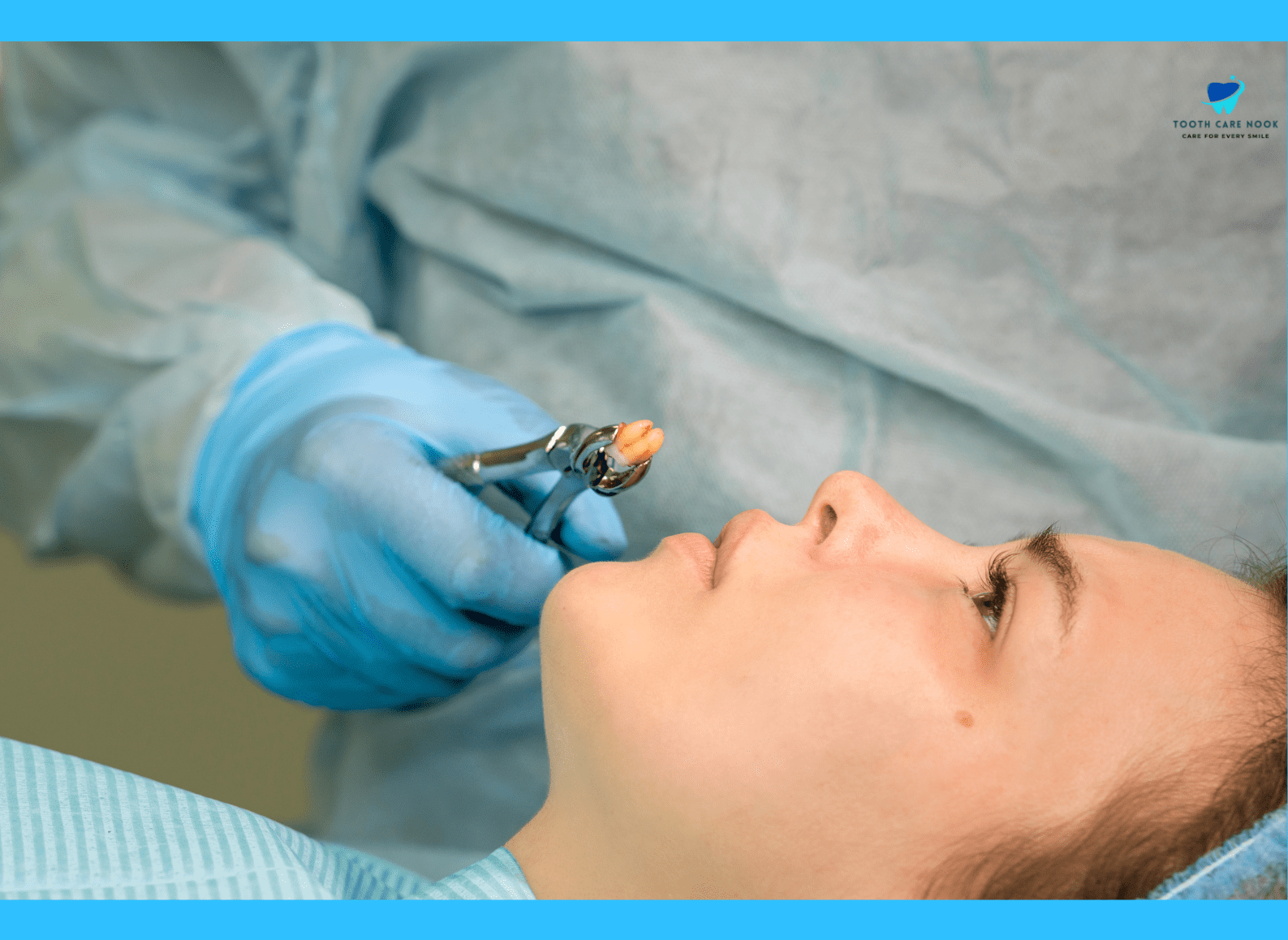
What Is Intrusive Luxation?
This is a specific type of dental injury where a tooth gets pushed inwards due to impact or trauma. However, unlike a general intrusion, intrusive luxation involves a deeper displacement of the tooth beyond its normal socket depth within the jawbone. This forceful movement can cause significant damage to the surrounding bone, blood vessels, and nerves.
Intrusive Luxation Vs Intruded Teeth
| Intruded Teeth | Intrusive Luxation |
| Within the normal socket depth | Beyond the normal socket depth |
| Bone damage is possible but usually minimal | Significant damage likely |
| Less likely nerve/blood vessel damage | More likely due to deeper displacement |
| Intruded teeth’s treatment complexity may vary depending on the severity | Typically more complex due to extensive damage |
FAQs
Should I Be Worried If My Child’s Primary Tooth Intrusion?
Primary tooth intrusions are generally less worrisome than permanent intrusion of teeth while any dental injury is concerning. This is because primary teeth are naturally designed to be shed and replaced by permanent teeth later. But, it’s still important to see a dentist to assess the situation.
How Can I Stop My Teeth From Spreading?
You should maintain good oral hygiene and wear a retainer to stop your teeth from spreading. Consistent retainer use can help maintain alignment and prevent teeth from shifting if you have braces or other orthodontic treatment.
Will My Child’s Intruded Baby Tooth Come Back?
No, a baby tooth will not grow back after being intruded. However, the permanent tooth developing beneath it should not be affected and will erupt in its place when the time comes.
What Is The Best Vitamin For Teeth?
There isn’t a single best vitamin for teeth. However, a well-balanced diet rich in calcium, vitamin D, and other essential nutrients is a must for strong teeth development and overall oral health.
What Happens If The Dentist Extracts My Child’s Intruded Baby Tooth?
If the dentist determines extraction is necessary for a severely intruded baby tooth, there’s usually no cause for alarm. The permanent tooth developing underneath should erupt in its place naturally when the time comes. However, the dentist might recommend monitoring or space maintainers to ensure proper eruption of the permanent tooth depending on the timing and location of the extraction.